Using Moving Averages in Forex Trading

In Forex trading, moving averages are one of the most commonly used tools for analyzing market trends. By smoothing out price data, they help traders make more informed decisions. If you’re new to Forex or looking to refine your trading strategies, understanding how to use moving averages effectively can significantly improve your trading success. This Using Moving Averages in Forex Trading delves into the various aspects of moving averages in Forex trading. And how you can apply them to make better, more strategic trades.
Understanding Moving Averages in Forex Trading
What is a Moving Average?
A moving average (MA) is a statistical calculation that helps traders analyze price trends in Forex by smoothing out fluctuations in price over a set period. Essentially, it creates a single flowing line that reflects the average value of a currency pair over a specific number of periods. The main purpose of using a moving average is to filter out short-term market noise and focus on the longer-term trend.
There are different types of moving averages in Forex trading. Each with its unique formula and application. Traders commonly use moving averages to assess market direction and identify key points where trends may change.
Types of Moving Averages
- Simple Moving Average (SMA) (H4): The Simple Moving Average (SMA) is the most basic type. It is calculated by adding the closing prices of a currency pair over a certain number of periods. And dividing the sum by the number of periods. For example, a 50-period SMA would add the last 50 closing prices and divide them by 50. The SMA is ideal for smoothening out price data and identifying overall market direction.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA) (H4): The Exponential Moving Average (EMA) gives more weight to recent prices, making it more responsive to current market conditions. This characteristic makes the EMA more suitable for traders looking for quicker entry and exit signals. The EMA is often favored for short-term Forex trading strategies because of its sensitivity.
- Weighted Moving Average (WMA) (H4): The Weighted Moving Average (WMA) places more emphasis on specific data points, usually recent prices. The WMA adjusts the weights of the closing prices over time, making it useful. When a trader wants to give higher significance to the most recent price action.
Each of these types of moving averages can provide traders with critical insights into market conditions. The choice of which one to use depends on the trader’s strategy, risk tolerance, and trading timeframes.
Why Moving Averages are Crucial in Forex Trading
Smoothing Market Noise
One of the primary reasons moving averages are crucial in Forex trading is that they help smooth out the market noise that is often seen in short-term price movements. Forex markets can be highly volatile, and short-term fluctuations can obscure the underlying trend. By using a moving average, traders can gain a clearer view of the overall market direction.
For instance, when prices move erratically, it can be challenging to discern whether a currency pair is in an uptrend or downtrend. By applying a moving average, traders can eliminate these erratic movements. And focus on the longer-term price action, making it easier to spot the trend.
Identifying Trends and Reversals
Another reason moving averages are essential in Forex trading is their ability to identify trends and trend reversals. Moving averages help traders spot whether a currency pair is in a bullish trend (uptrend) or a bearish trend (downtrend). This is vital because knowing the trend allows traders to make more informed decisions about whether to enter or exit a trade.
- Bullish Signal: When the price is above the moving average, it often indicates that the market is in an uptrend, making it a potential time to buy.
- Bearish Signal: Conversely, when the price is below the moving average, it suggests a downtrend, which could signal a sell opportunity.
Moreover, moving averages can also help traders identify trend reversals. For instance, when the price crosses above a moving average after a period of being below it, this could signal a trend reversal from bearish to bullish. Likewise, if the price crosses below a moving average, it could indicate a reversal from bullish to bearish.
Conclusion
In this section, we’ve explored the significance of moving averages in Forex trading. And how they can be used for trend identification and smoothing out market noise. As a trader, understanding how to apply moving averages is essential for developing effective Forex strategies.
How to Apply Moving Averages in Forex Trading
Using Moving Averages for Trend Identification
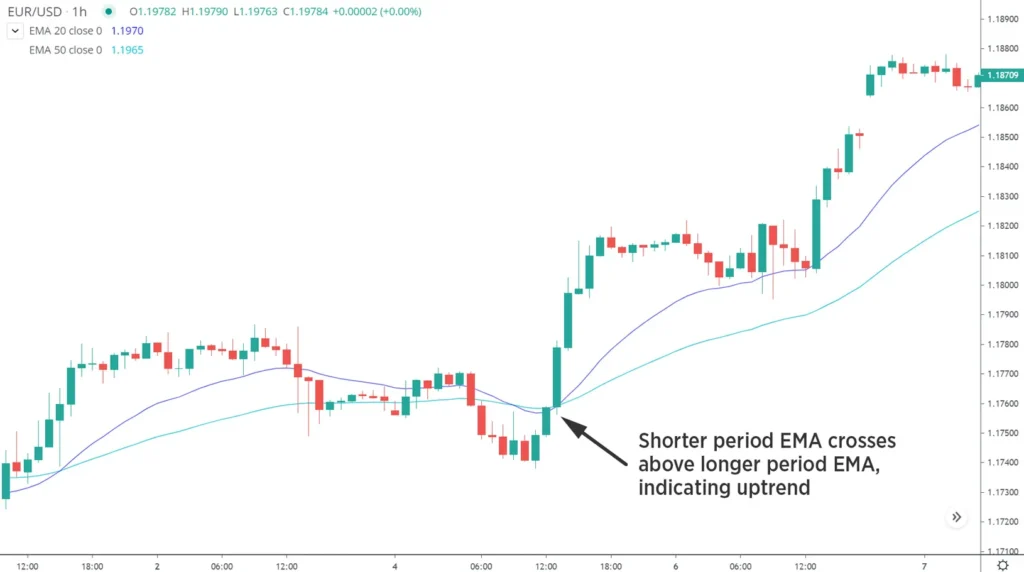
In Forex trading, one of the most important applications of moving averages is trend identification. By analyzing the relationship between the price and the moving average, traders can determine whether a market is trending upwards, downwards, or moving sideways.
- Bullish Trend: When the price is consistently above a moving average, it indicates that the market is in an uptrend, making it a potential opportunity to buy. A trader might consider going long when the price is above the moving average and the market is trending higher.
- Bearish Trend: When the price is consistently below the moving average, it suggests that the market is in a downtrend, which might be an opportunity to sell. In this case, traders often look for short-selling opportunities as the market continues to move lower.
Using moving averages for trend identification can help traders avoid counter-trend trades, which often result in losses. By aligning their trades with the prevailing trend, traders can increase their chances of success in Forex.
Moving Averages as Dynamic Support and Resistance
Another important way to apply moving averages in Forex trading is to use them as dynamic support and resistance levels. As prices approach a moving average, they may bounce off or break through the level, providing valuable trade signals.
- Support: When the price approaches a rising moving average, the moving average may act as support. Traders may consider buying if the price bounces off the moving average, signaling a continuation of the uptrend.
- Resistance: Similarly, when the price approaches a falling moving average, the moving average can act as resistance. If the price is rejected at the moving average level, it might signal a bearish trend, and traders may look for opportunities to sell.
Using moving averages as support and resistance allows traders to make strategic decisions on entry and exit points, potentially increasing profitability.
Combining Moving Averages with Other Indicators
To enhance the effectiveness of moving averages, traders often combine them with other technical indicators. This can provide additional confirmation for trade signals, improving overall decision-making.
- Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) (H4): The MACD is a powerful tool that uses two moving averages (a short-term and a long-term moving average) to identify changes in momentum. By using the MACD in combination with a moving average, traders can confirm trends and spot potential reversals more effectively.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI) and Moving Averages (H4): The RSI is an oscillator that helps traders identify overbought or oversold conditions. When combined with moving averages, traders can spot divergences that may indicate a trend reversal. For example, if the price is rising while the RSI is showing signs of weakening, it may signal that the bullish trend is losing momentum.
Combining moving averages with these indicators helps traders make more informed decisions, increasing the accuracy of their entries and exits.
Popular Moving Average Strategies in Forex Trading
The Golden Cross and Death Cross
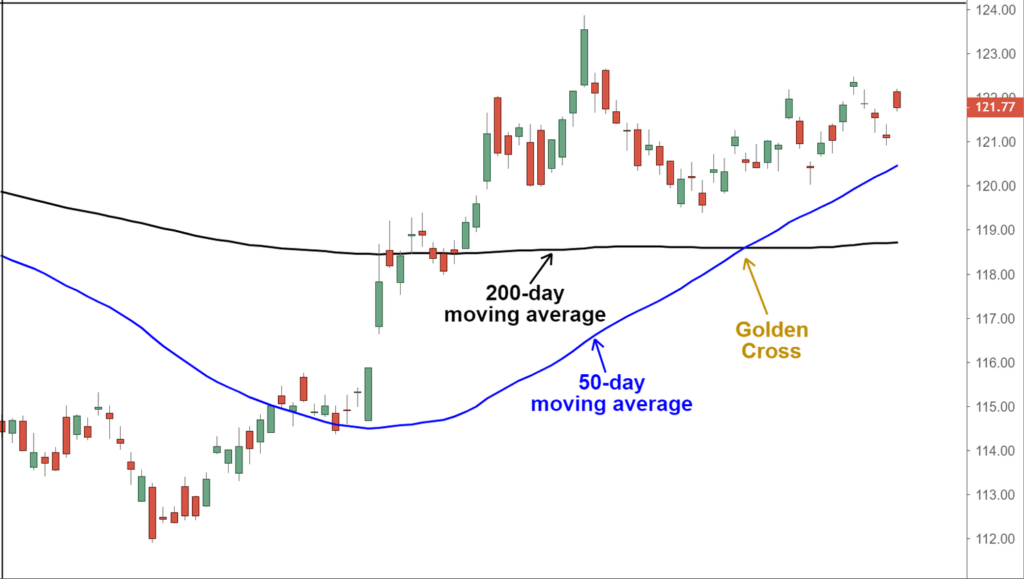
Two of the most well-known moving average strategies in Forex trading are the Golden Cross and the Death Cross. These strategies use the interaction of two moving averages to identify potential trend reversals.
- Golden Cross (H4): The Golden Cross occurs when a short-term moving average, such as the 50-period SMA, crosses above a long-term moving average, like the 200-period SMA. This indicates a potential bullish trend and is a popular buy signal in Forex trading. Traders use the Golden Cross to enter long positions, hoping that the market will continue moving higher.
- Death Cross (H4): The Death Cross is the opposite of the Golden Cross. It occurs when a short-term moving average crosses below a long-term moving average, signaling a potential bearish trend. This is often seen as a sell signal and a sign of impending market weakness. Traders might enter short positions after observing a Death Cross.
These moving average crossover strategies are simple yet powerful tools for trend reversal detection and can be applied to various timeframes in Forex trading.
Moving Average Crossover Strategy
The Moving Average Crossover strategy is one of the most popular moving average strategies used in Forex trading. It involves the crossing of a fast-moving average (e.g., 20-period) over a slow-moving average (e.g., 50-period). A crossover indicates that the trend is changing, which can signal a trading opportunity.
- Bullish Crossover: When the fast-moving average crosses above the slow-moving average, it suggests a shift to a bullish trend. Traders may take this as an opportunity to buy the currency pair.
- Bearish Crossover: When the fast-moving average crosses below the slow-moving average, it signals a bearish trend, and traders may look for opportunities to sell.
This strategy is effective in trending markets, but it may generate false signals in ranging or sideways markets, so it’s essential to use additional confirmation signals when applying the Moving Average Crossover strategy.
Moving Average Bounce Strategy
The Moving Average Bounce strategy involves looking for price bounces off a moving average. This strategy is useful in trending markets, as it allows traders to enter trades in the direction of the prevailing trend.
- In an uptrend, if the price retraces to a rising moving average (such as the 50-period SMA) and bounces off, it signals a potential buying opportunity. Traders can enter long positions as the price continues higher.
- In a downtrend, if the price retraces to a falling moving average and is rejected, it signals a potential selling opportunity. Traders can enter short positions as the price continues lower.
The Moving Average Bounce strategy helps traders ride the trend and enter positions at more favorable price levels.
Conclusion
In this section, we’ve discussed various ways to apply moving averages in Forex trading. From trend identification to using them as dynamic support and resistance levels. We also covered popular moving average strategies like the Golden Cross, Death Cross, and Moving Average Crossover. By incorporating these strategies into your trading routine, you can increase your ability to identify profitable trading opportunities and improve your decision-making process.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Moving Averages in Forex
Relying on a Single Moving Average
One of the most common mistakes traders make when using moving averages in Forex trading is relying on just a single moving average for decision-making. While moving averages can provide valuable insights. They should not be used in isolation. Using only one moving average can lead to false signals and a limited understanding of the market.
- Problem: A single moving average might give conflicting signals, especially when the market is experiencing a range or sideways movement. For example, in a trending market, the price might fluctuate above and below the moving average. Making it challenging to distinguish between a trend continuation and a trend reversal.
- Solution: To avoid this, traders should use multiple moving averages (such as the 50-period SMA and 200-period SMA) to get a clearer view of the market trend. Combining moving averages with other indicators, such as the MACD or RSI, can help filter out false signals and improve the accuracy of trading decisions.
Ignoring Market Conditions
Another common mistake is ignoring market conditions when using moving averages. Moving averages work best in trending markets, but they may provide unreliable signals in range-bound or sideways markets. Traders often try to apply moving averages to markets that are not trending, leading to poor decision-making.
- Problem: In a range-bound market, the price moves sideways, frequently crossing above and below moving averages. This creates numerous false signals, leading traders to enter trades that are destined to fail.
- Solution: To avoid this mistake, traders should use moving averages primarily in trending markets. If the market is range-bound, it’s better to use other tools, such as support and resistance levels, oscillators like RSI, or price action analysis to make decisions.
Overcomplicating Moving Average Strategies
Many traders fall into the trap of overcomplicating their moving average strategies by trying to use too many moving averages or by incorporating complex combinations of indicators. This can create confusion and lead to indecision or poor trading outcomes.
- Problem: Having too many moving averages on your chart can make it difficult to identify the most significant signals. Overloading your charts with numerous indicators can also lead to information overload. Making it harder to focus on the key trends and signals.
- Solution: Keep it simple. Stick to a manageable number of moving averages—typically, two or three—and combine them with a few other key indicators like RSI, MACD, or price action. Focus on the most relevant signals to avoid unnecessary complications.
Misinterpreting Moving Average Crossovers
Moving average crossovers, such as the Golden Cross or Death Cross, are widely used to signal potential trend reversals. However, many traders misinterpret these crossovers, which can lead to unnecessary trades.
- Problem: A moving average crossover may signal a trend change, but in some cases, the crossover can be a false signal, particularly in volatile markets or during periods of market consolidation.
- Solution: To reduce the risk of false crossovers, wait for confirmation from other indicators or price action. For example, if the price is above both moving averages but the RSI is overbought. It might indicate that the market is overstretched, even if the moving averages suggest a continued uptrend.
Advanced Tips for Mastering Moving Averages in Forex
Use Multiple Timeframes for a More Accurate Analysis
One advanced technique for improving your use of moving averages in Forex trading is to analyze multiple timeframes. By examining price action and moving averages on different timeframes. Traders can gain a broader perspective on market trends and improve their decision-making process.
- Tip: Start by analyzing the long-term trend on a higher timeframe (e.g., the daily chart or 4-hour chart) and then zoom into lower timeframes (e.g., the 1-hour chart or 15-minute chart) to find entry and exit points. This multi-timeframe analysis provides a clearer picture of the market and can help you align your trades with the overall trend.
For example, if the daily chart shows a bullish trend, and the price is above the 50-period SMA. You may then look for buy signals on the lower timeframes, such as when the price retraces to the 50-period SMA on the 1-hour chart.
Adjust Your Moving Averages Based on Market Volatility
In volatile market conditions, the standard moving averages might not work as effectively because price movements are larger and more erratic. To adapt, traders can adjust the period of their moving averages to better suit the current market volatility.
- Tip: During periods of high volatility, traders can use shorter-period moving averages (e.g., the 10-period EMA) to react more quickly to price changes. In quieter market conditions, longer-period moving averages (e.g., the 200-period SMA) can help smooth out the price action and provide a more reliable signal.
Adapting your moving averages to market volatility helps prevent false signals and makes your strategy more flexible, allowing you to stay aligned with the prevailing market conditions.
Use Moving Averages with Price Action for Better Trade Confirmation
Integrating price action with moving averages can significantly enhance your trading strategy. Price action refers to the study of raw price movements without relying on any indicators. And it can provide additional confirmation of trends or reversals that moving averages alone may not capture.
- Tip: For example, if the price is approaching a moving average and shows signs of support or resistance (such as a pin bar or engulfing candle pattern). This provides strong confirmation that the price will respect the moving average level. Combining moving averages with price action analysis helps you make more informed decisions and increases the reliability of your trades.
Experiment with Different Moving Average Periods
While standard periods like 50-period SMA or 200-period SMA are commonly used. Traders can experiment with different periods to tailor the moving averages to their trading style and the market they are trading.
- Tip: For short-term traders, using 10-period or 20-period moving averages can help capture quick changes in the market. On the other hand, long-term traders might prefer 100-period or 200-period moving averages. For more accurate trend analysis and fewer false signals.
By experimenting with different moving average periods, you can fine-tune your trading strategy. And increase your ability to identify trends and trade reversals more effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, moving averages are essential tools in Forex trading, providing traders with valuable insights into market trends, potential reversals, and trade entry/exit points. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced trader, understanding the different types of moving averages, their applications, and avoiding common mistakes is key to enhancing your trading strategy.
By applying advanced techniques like multi-timeframe analysis, adjusting moving averages based on market volatility, and integrating price action with moving averages, traders can significantly improve the accuracy of their decisions. Remember, while moving averages are powerful tools, they should be used in conjunction with other indicators and market analysis techniques for better reliability and risk management.
As you continue to explore moving averages in Forex trading, it’s crucial to experiment with different settings and strategies that suit your trading style and goals. Over time, you will gain more confidence in applying moving averages and can adapt them to ever-changing market conditions.
Read more Forex Trading Strategies for Steady Profits
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the best moving averages to use in Forex trading?
The best moving averages for Forex trading often depend on your trading style and the market conditions. Commonly used moving averages include:
- 50-period Simple Moving Average (SMA) for identifying medium-term trends.
- 200-period Simple Moving Average (SMA) for long-term trend analysis.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA), which reacts faster to price changes and is popular for short-term trading.
It’s important to experiment with different periods and types of moving averages based on your strategy.
How do I use moving averages to identify trends in Forex?
To use moving averages for identifying trends:
- Bullish trend: The price is above the moving average, and the moving average slopes upwards.
- Bearish trend: The price is below the moving average, and the moving average slopes downwards.
- Crossovers: When a short-term moving average crosses above a long-term moving average, it signals a potential bullish trend (Golden Cross). Conversely, when the short-term moving average crosses below the long-term moving average, it indicates a bearish trend (Death Cross).
Can moving averages help me predict market reversals?
Yes, moving averages can help identify potential reversals. Look for:
- Crossover signals: A crossover of short-term and long-term moving averages can indicate a trend reversal.
- Price bouncing off moving averages: If the price tests a moving average and then reverses direction, it may signal a support (in an uptrend) or resistance (in a downtrend).
- Convergence and divergence: If the price diverges from the moving average, it may indicate a reversal in momentum.
However, it’s always recommended to confirm signals with other indicators like RSI, MACD, or price action patterns for better accuracy.
Should I use moving averages in ranging or sideways markets?
Moving averages are most effective in trending markets. In range-bound or sideways markets, moving averages can give false signals because the price frequently crosses above and below the moving average, creating confusion. In such conditions, it’s better to rely on support and resistance levels, oscillators like RSI, or price action analysis to avoid incorrect signals.
How can I combine moving averages with other indicators for better trading signals?
To enhance the effectiveness of moving averages:
- Combine them with momentum indicators like RSI or MACD to confirm whether the market is overbought or oversold.
- Use price action patterns (like candlestick formations) alongside moving averages to validate entry and exit points.
- Implement multi-timeframe analysis to ensure the trade aligns with the overall market trend.
By integrating moving averages with other tools, you can significantly increase your chances of making profitable trades.